Age assurance
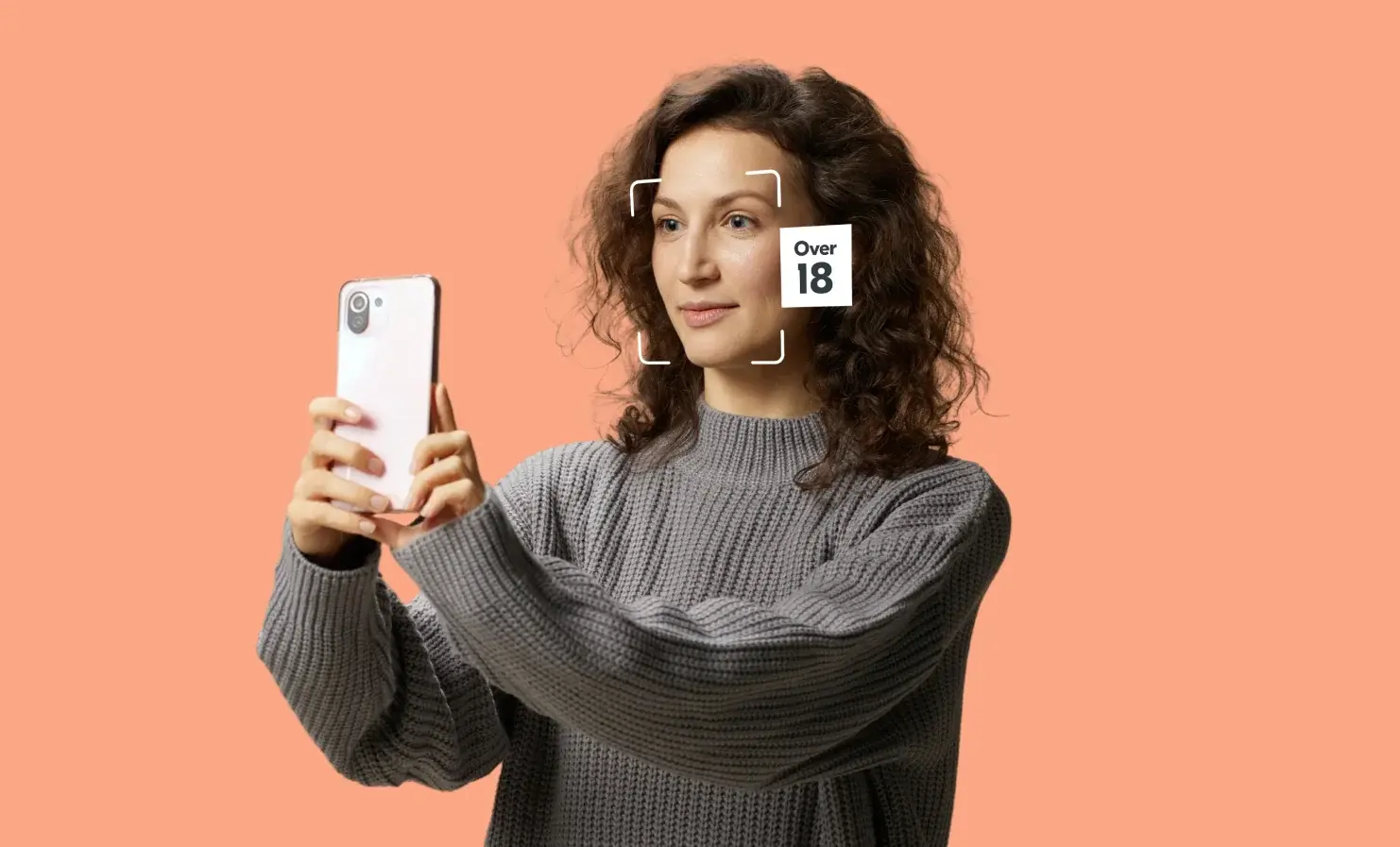
Yoti facial age estimation - newest model evaluation by NIST
We are delighted to share our latest evaluation by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) for our newest facial age estimation model. We have seen notable performance improvements across a number of metrics. NIST’s evaluation is extremely thorough – they have over 20 million images for evaluation – and NIST develops their testing methodology over time. This helps to highlight models that are robust across multiple datasets and scenarios. Our strategy for developing our model is not “data dependent”. Machine learning models can benefit greatly from quantity of data at the initial stage, but once reaching maturity,
Yoti age tokens, passkeys and privacy: Reflections on 6 years of scaling privacy-preserving age assurance
Over recent months, there’s been growing buzz in the industry about privacy-preserving ways to prove age online. Device-bound age tokens, passkey-binding and cryptographic signals that confirm someone is “over 18” without sharing any identity details are increasingly being discussed as if they’re brand new ideas. It’s great to see this conversation picking up. The online world needs ways for people to prove their age in seconds, with minimal data and maximum privacy. But it’s worth adding a bit of context. Yoti age tokens have been around since 2019 We introduced Yoti age tokens back in 2019. These are
Yoti helps platforms navigate Australia’s new social media age restrictions
Australia’s new age restriction laws for social media come into effect today, signalling a major shift in how online services must support age-appropriate access for younger users. As platforms prepare for increased regulatory scrutiny and tight compliance timelines, Yoti is enabling our social media partners to deploy trusted, privacy-preserving age assurance at scale. These reforms, led by the eSafety Commissioner, require major social media platforms to take ‘reasonable steps’ to stop under 16s from creating an account or using their services. There are no exceptions to this age limit, not even those with parental consent. The rules apply to
Keep calm and carry on - what to expect ahead of Australia's age checks for social media
We’ve been talking to a number of media outlets ahead of Australia’s upcoming social media ban for under 16’s – set to kick in on 10th December – and thought it was worth sharing our insights more widely. After all, there’s plenty of speculation about what will actually happen: Will systems cope? Will there be issues accessing sites? Will everything grind to a halt? After supporting a number of countries across the world as they’ve rolled out age assurance measures (including the UK Online Safety Act’s launch in July this year), we can say with confidence that the infrastructure
Yoti completes 1 billion age checks - and counting!
We’re celebrating a huge moment in our journey: Yoti has now completed over 1 billion age checks! When we started out, we had a simple but powerful ambition: to help people prove their age without revealing their full identity. We recognised early on that not everyone has access to a document or always feels comfortable using it. That’s why we innovated and developed facial age estimation. Reaching this milestone – across facial age estimation, Digital IDs, identity document checks and our other secure age-checking methods – shows that our technology is being used safely and responsibly around the
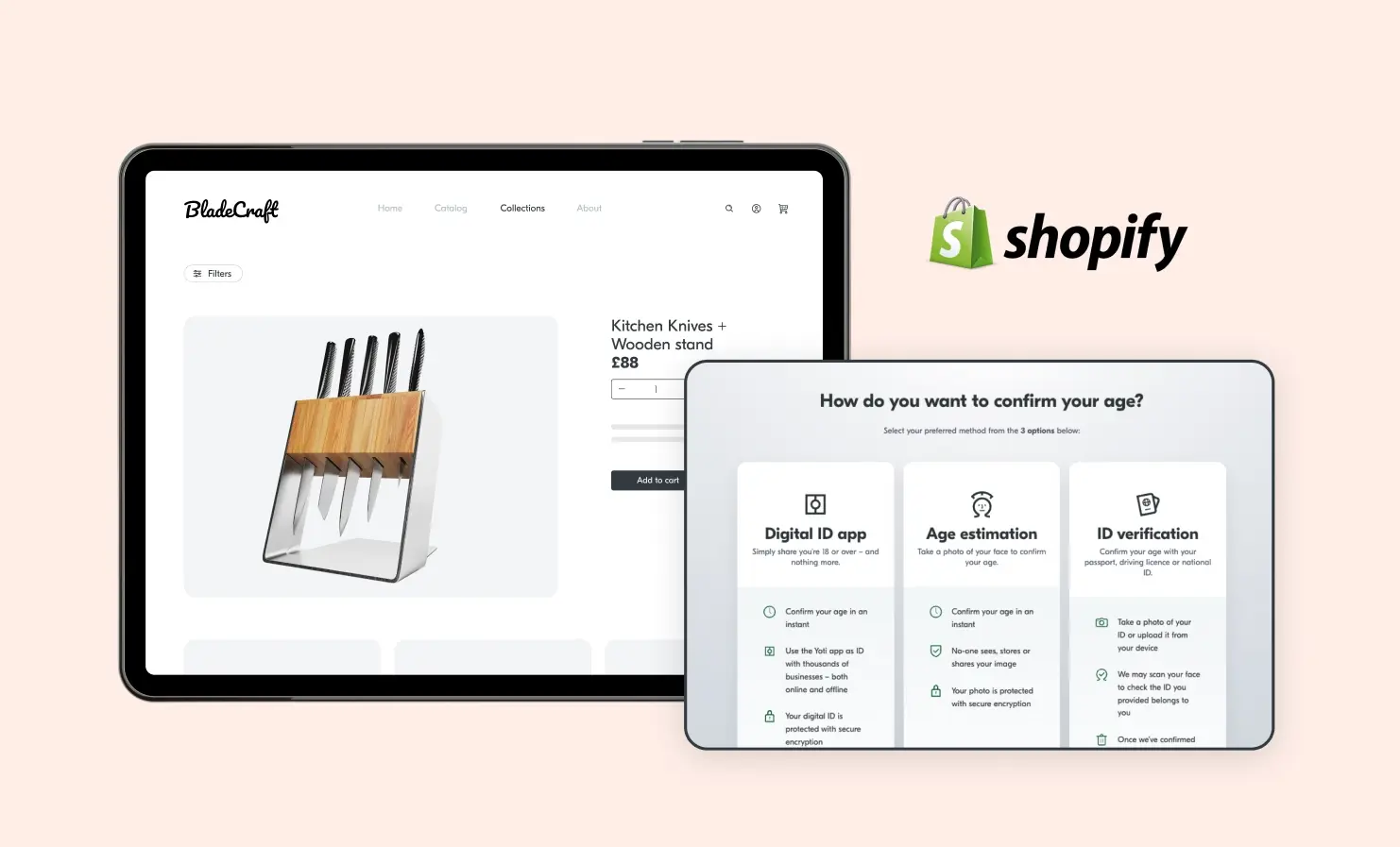
Yoti age checks now available for Shopify stores
If you sell age-restricted products on Shopify, we’ve got good news. It’s now easier than ever to add secure, seamless age checks to your online store. Yoti has now officially integrated with Shopify – one of the biggest ecommerce platforms in the world. That means Shopify merchants can now offer fast, privacy-preserving age checks for their customers. If you’re selling alcohol, vapes, knives or other age-restricted items, this integration helps you meet legal requirements without adding unnecessary friction to your customers’ journey. Why does this matter for Shopify merchants? Shopify powers millions of online businesses, including both independent