Back in the day, identity theft mostly involved fraudsters stealing personal information, such as credit card details, to commit fraud or impersonate others in person. It was a pretty straightforward game of cat and mouse between scammers and a business, typically carried out face-to-face.
As the world has become more digitised, identity fraud has evolved to meet this digital world.
One powerful solution in our arsenal against biometric frauds is biometric verification. Let’s dive into what it is, how it works, and why it’s crucial for keeping your customers and online community safe.
What is identity fraud?
Identity fraud is the unauthorised use of a person’s information for fraud. It occurs, particularly in the context of biometrics, when scammers use someone else’s biometric information to impersonate that individual or create a new fake identity.
This stolen identity is then used to gain access to online systems or services to commit criminal activities.
Here are typical examples of identity scam in the digital world:
Impersonation attacks
Impersonation attacks happen when fraudsters use stolen or replicated biometric data, such as facial images, to impersonate a legitimate person.
A common example is a phishing email, in which an attacker poses as a legitimate company or important person to trick the recipient. They may request the recipient to urgently click on a link or enter their login credentials on a fake site. If the recipient falls for it, sensitive data is shared with fraudsters.
There are many more types of impersonation attacks, one of which is CEO fraud. Fraudsters impersonate a company’s CEO and try to convince employees or customers that they need access to sensitive information urgently.
Account takeover
Account takeover occurs when fraudsters obtain and use someone else’s credentials to take over legitimate user accounts or access sensitive information, such as financial accounts or personal records, without the person’s consent.
Fraudsters often use bots to carry out large-scale attacks, such as credential stuffing. In this technique, fraudsters use bots to automate the testing of large volumes of stolen usernames and passwords. These bots test those credentials to gain access across multiple online accounts, such as email, banking, or shopping accounts.
Synthetic identities
The creation of synthetic identities involves fraudsters blending real and fabricated details to create a new fake identity, which enables them to open fraudulent accounts, apply for loans, or commit other forms of financial fraud.
The quality of fake digital IDs generated by AI has reached an alarming level of sophistication. It’s now cheap and easy for anyone to create or buy digital fakes, with fraudsters producing masses of these IDs within minutes to meet demand.
A known underground website is the latest player in this arena. It claims to use “neural networks” to create highly convincing synthetic IDs for just $15.
Deepfake fraud
Deepfake fraud represents the latest evolution in the progress of fraudulent misuse of technology. Fraudsters use Artificial Intelligence (AI) to produce deepfakes—realistic videos or images manipulated using advanced algorithms to mimic real people. These manipulated visuals and audio clips show people engaging in actions or making statements they never did. Or used for online dating scams.
For example, these fakes impersonate individuals in video calls to obtain sensitive financial information or damage someone’s reputation. Notable examples include deepfakes of singer Taylor Swift and President Joe Biden.
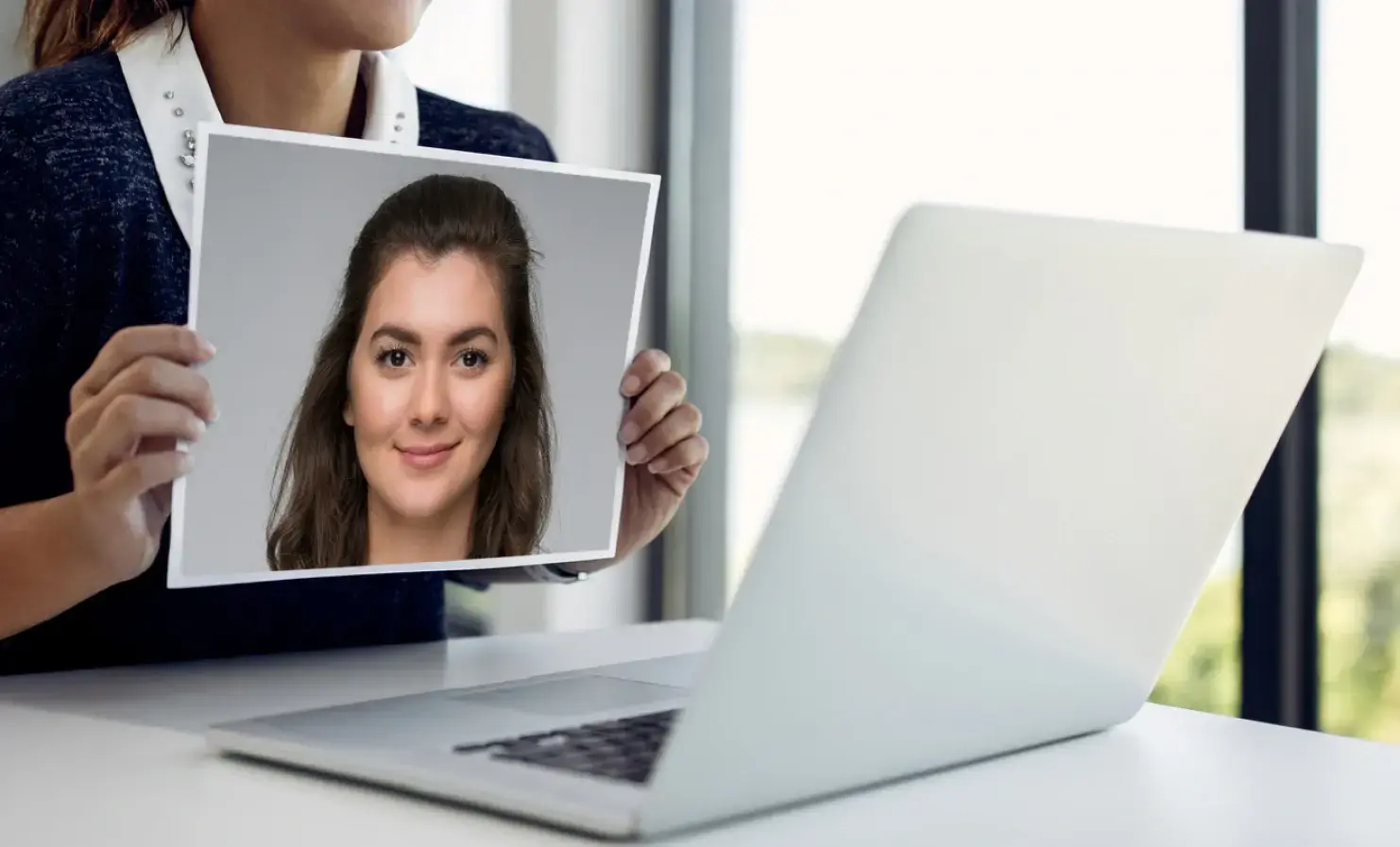
Another way deepfakes are used is to attempt to spoof a business’s biometric verification system’s liveness detection, which checks that a real person is present. Two types of attacks aim to deceive biometrics by defeating liveness detection: presentation attacks and injection attacks.
Presentation attacks involve presenting non-live imagery as live using physical media, such as photos and digital screens, during the liveness capture part of a verification process.
Injection attacks are a type of hardware or software hack that allows fraudsters to trick a security system by inserting imagery that bypasses the image capture process. Injection attacks are a growing threat to online verification processes. Fraudsters attempt to bypass liveness detection by injecting manipulated images, videos, or even artificially generated content to spoof authentication systems.
As fraudsters continue to change their tactics, businesses must also update their defences against identity fraud.
Understanding facial biometric verification
Digital identity verification has become crucial for businesses operating in the digital world, and biometric verification offers an advanced solution for verifying individuals online.
This type of verification offers a powerful way to confirm someone’s identity by analysing their unique physical and biological traits. These traits include fingerprints, facial features and voice patterns. While many people are familiar with using their fingerprints or faces to unlock smart devices, biometric authentication encompasses a broader range of biological characteristics, such as retinal scans and voice recognition.
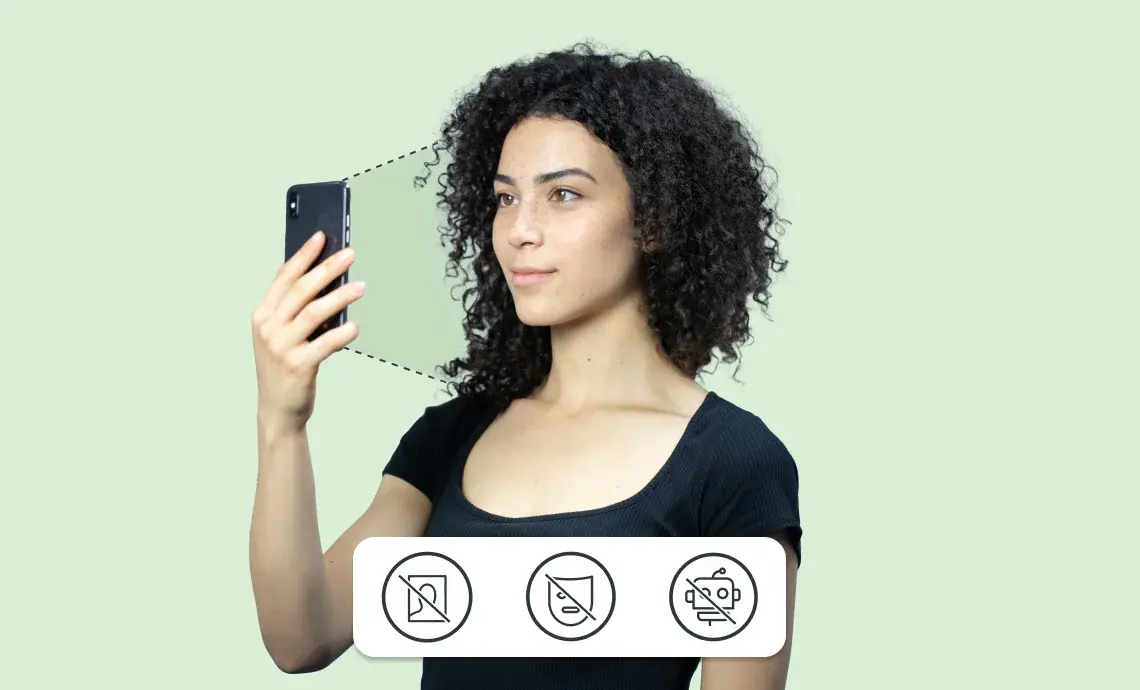
Facial biometric verification is a highly secure method that enables effective digital identity verification to combat fraud. Using unique facial traits that are difficult to replicate or steal helps reduce fraudulent attempts in online spaces. It provides better protection against identity fraud than traditional methods like passwords or PINs, which are easily forgotten, stolen, or guessed.
Anti-spoofing technology is a key factor in preventing attacks. This technology verifies the presence of a live person in an image or video without identifying them, ensuring the process remains secure and responsive only to genuine human faces.
Anti-spoofing methods come in two types: active and passive liveness.
Active liveness requires users to perform specific actions to analyse their movement, distinguishing real individuals from those wearing masks. Passive liveness operates discreetly in the background, analysing a single image to detect real individuals behind the camera without their awareness, making it challenging for fraudsters to spoof.
Facial biometric verification methods combine advanced AI technology to make online identity verification more user-friendly and authentication more robust.
Advantages of using facial biometrics for fraud prevention
In the ongoing fight against fraud, biometric authentication serves as a business’ ultimate defence in identity verification. By implementing it, you can:
- Enhance security: Biometric data is unique to each individual, making it extremely difficult for fraudsters to impersonate someone else, which reduces the risk of identity theft.
- Simplify authentication: Passwordless authentication eliminates the need for passwords or PINs, streamlining the process for users and decreasing the risk of phishing attacks.
- Ensure robust fraud detection: Use real-time monitoring to detect and prevent fraudulent activities and better safeguard against identity theft and financial fraud attempts.
MyFace AI services, the ultimate defence against fraud
To effectively combat fraud, businesses across every industry, especially financial institutions and financial services, must distinguish between genuine customers and fraudulent actors. However, tackling fraud requires a nuanced and multi-layered approach to onboarding to effectively prevent criminal activity from entering your online community or services.
Our MyFace AI services are your ultimate defence against fraudsters attempting to spoof your systems. Each AI service strengthens your existing verification and authentication processes. Our suite of complementary solutions tackles various levels of fraud, from sophisticated AI-generated deepfakes to identity document fraud.
MyFace AI services provide robust protection against presentation attacks, bots, deepfakes, and injection attacks, ensuring the security of your business while providing a seamless customer experience.
Discover more about our MyFace AI services and how each can strengthen your business against every type of fraud.